CloudTrail Lake - Deployment to EKS
This guide offers 2 methods to deploy the Falcon Integration Gateway into an existing EKS Cluster. You
can choose to either deploy the FIG container with a Helm chart, or as a standard Kubernetes pod spec
file.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- Falcon API Credentials
- Your cluster has an OpenID Connect (OIDC) issuer URL associated with it.
This is necessary to properly create the IAM role for the service account used in the FIG. For
more information, view the AWS
documentation on this.
Create the IAM Role for the Service Account
-
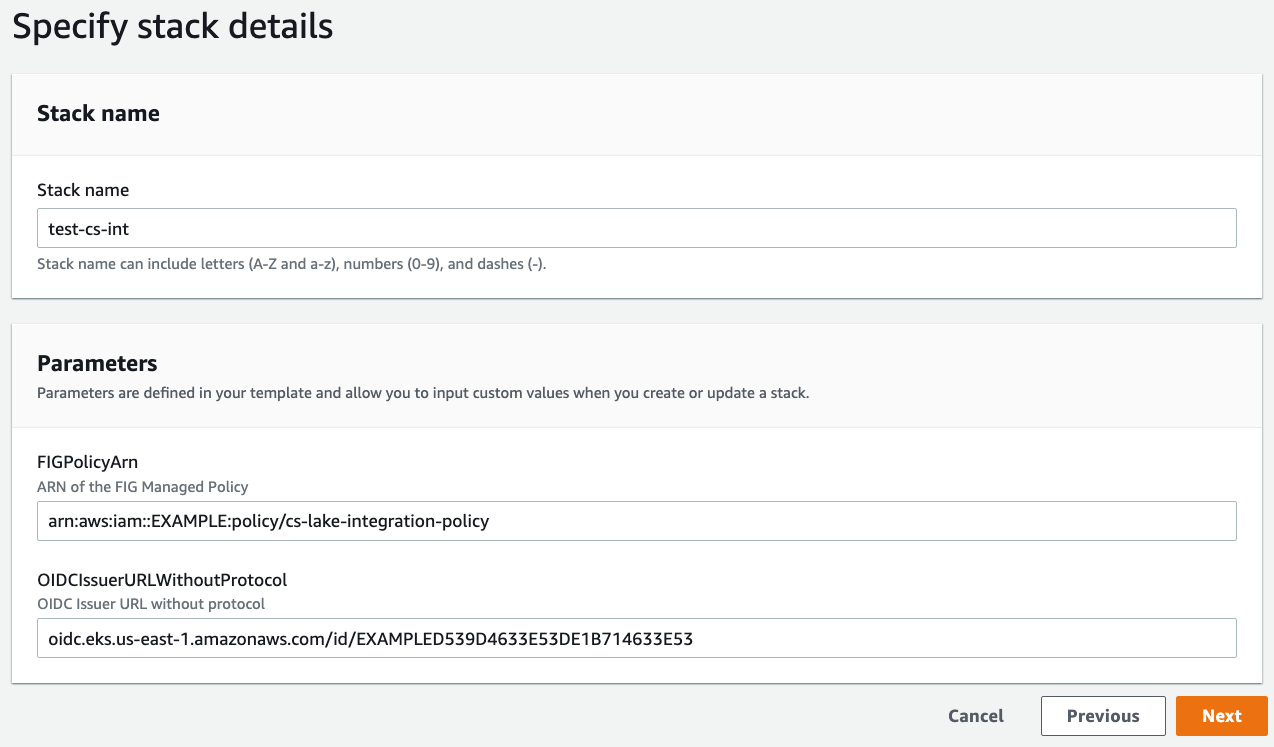
Please use the CloudFormation Template to create your service account IAM Role.
The screenshot below is an example.
Please note the OIDCIssuerURLWithoutProtocol does not have a protocol (http |
s://). |
The FIGPolicyArn is from the CloudTrail Lake Integration Getting Started guide
- Once the CloudFormation stack is completed, in the Outputs tab, make note of the
FalconFigAccessRoleArn value.
This value will be used as an input when deploying the FIG application on EKS.
Choose Your Method
Deployment to EKS using Helm Chart
Click to expand
#### Prerequisite
For Dependency requirements, installation instructions, as well as the full list of available configuration options, go to
the [Helm Chart - Falcon Integration Gateway](https://github.com/CrowdStrike/falcon-helm/tree/main/helm-charts/falcon-integration-gateway)
repository.
##### Export the following variables
```bash
export FALCON_CLIENT_ID=
export FALCON_CLIENT_SECRET=
export FALCON_CLOUD_REGION=
export CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_CHANNEL_ARN=
export CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_REGION=
export FALCON_APPLICATION_ID=
export IAM_ROLE_ARN=
```
#### Installation
1. Add the CrowdStrike Falcon Helm repository
```bash
helm repo add crowdstrike https://crowdstrike.github.io/falcon-helm
```
2. Update the local Helm repository cache
```bash
helm repo update
```
3. Install the FIG with AWS CloudTrail Lake enabled:
```bash
helm install falcon-fig crowdstrike/falcon-integration-gateway -n falcon-integration-gateway --create-namespace \
--set falcon.client_id=$FALCON_CLIENT_ID \
--set falcon.client_secret=$FALCON_CLIENT_SECRET \
--set falcon.cloud_region=$FALCON_CLOUD_REGION \
--set falcon.integration_gateway.application_id=$FALCON_APPLICATION_ID \
--set push.cloudtrail_lake.enabled=true \
--set push.cloudtrail_lake.channel_arn=$CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_CHANNEL_ARN \
--set push.cloudtrail_lake.region=$CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_REGION \
--set serviceAccount.annotations."eks\.amazonaws\.com/role-arn"=$IAM_ROLE_ARN
```
#### Uninstall Helm Chart
To uninstall, run the following command:
```bash
helm uninstall falcon-fig -n falcon-integration-gateway
```
You may need/want to delete the falcon-integration-gateway namespace as well since helm will not do it for you:
```bash
kubectl delete ns falcon-integration-gateway
```
</details>
### Deployment to EKS with Pod Spec
Click to expand
#### Step 1: Edit Kubernetes Pod Spec
Download/Edit the pod specification file available [here](/falcon-integration-gateway/docs/cloudtrail-lake/eks/falcon-integration-gateway.yaml).
```bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/crowdstrike/falcon-integration-gateway/main/docs/cloudtrail-lake/eks/falcon-integration-gateway.yaml
```
Replace the credentials in the pod spec with the actual Falcon API credentials. The following commands illustrate how to base64 encode the credentials.
```bash
echo -n $FALCON_CLIENT_ID | base64
```
```bash
echo -n $FALCON_CLIENT_SECRET | base64
```
Replace the `` variable with the `FalconFigAccessRoleArn` output value from the cloudformation SA IAM role stack.
```yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: falcon-integration-gateway
namespace: falcon-integration-gateway
annotations:
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn:
```
##### ConfigMap Updates:
Uncomment the following variables in the `config.ini` ConfigMap:
> For more information about configuration options, refer to the FIG [config.ini](/falcon-integration-gateway/config/config.ini).
`channel_arn =` should be set to your provided CloudTrail Lake Channel ARN
`region =` should be set to your AWS region where you setup the CloudTrail Lake Channel
`application_id =` should be set to something unique.
> :exclamation: Running multiple FIG instances with the same `application_id` can cause issues.
See the below example of config changes:
Example config.ini
```bash
# Falcon Integration Gateway
[main]
# Cloud backends that are enabled. The gateway will push events to the cloud providers specified below
backends=CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE
# Uncomment to configure number of threads that process Falcon Events
#worker_threads = 4
[events]
# Uncomment to filter out events based on number of days past the event (default 21)
older_than_days_threshold = 14
[logging]
# Uncomment to request logging level (ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG)
#level = DEBUG
[falcon]
# Uncomment to provide Falcon Cloud. Alternatively, use FALCON_CLOUD_REGION env variable.
cloud_region = us-2
# Uncomment to provide application id. Needs to be different per each fig instance.
# Alternatively, use FALCON_APPLICATION_ID env variable.
application_id = fig-int-1
[cloudtrail_lake]
# AWS CloudTrail Lake section is applicable only when CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE backend is enabled in the [main] section.
# Uncomment to provide the Channel ARN. Alternatively, use CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_CHANNEL_ARN env variable.
channel_arn = arn:aws:cloudtrail:us-east-1:EXAMPLE:channel/EXAMPLE-9f94-471c-96ba-EXAMPLE
# Uncomment to provide the AWS region. Should match the same region as the Channel.
# Alternatively, use CLOUDTRAIL_LAKE_REGION env variable.
region = us-east-1
```
#### Step 2: Deploy to EKS
Ensure your kubectl command is configured to use your EKS environment
```bash
kubectl cluster-info
```
Deploy the pod
```bash
kubectl apply -f falcon-integration-gateway.yaml
```
A successful run should display:
```bash
namespace/falcon-integration-gateway created
secret/falcon-integration-gateway-creds created
configmap/falcon-integration-gateway-config created
serviceaccount/falcon-integration-gateway created
deployment.apps/falcon-integration-gateway created
```
#### Uninstall
To uninstall, run the following command:
```bash
kubectl delete -f falcon-integration-gateway.yaml
```
</details>
## Verify Deployment
Run the following commands to verify deployment was successful.
To verify pod health and get the pod name:
```bash
kubectl get pods -n falcon-integration-gateway
```
View the pod logs:
```bash
kubectl logs -n falcon-integration-gateway
```
A successful deployment should have logs that start with:
```bash
2022-09-15 19:52:35 fig MainThread INFO AWS CloudTrail Lake Backend is enabled.
2022-09-15 19:52:36 fig cs_stream INFO Opening Streaming Connection
...
...
```
